How Long Am I Contagious While I Have the Flu?
Flu season makes me think of sneezes, sniffles, chills, and that cough that just won’t go away. The scariest part? How long you are contagious and can spread the virus. There’s a lot of information out there on the internet about the flu - best practices, when to see a doctor, and how long to avoid people. I’ve compiled everything into this one blog post. Think of it as a “Tell-All” on the flu virus.

First, let’s begin with what the flu season technically is and what differentiates a flu from a cold.
According to the CDC, the flu season is year-round. Flu activity tends to increase during October and peaks in December and February. That’s why you will usually see CVS and Walgreens advertising their flu vaccine programs starting in September.
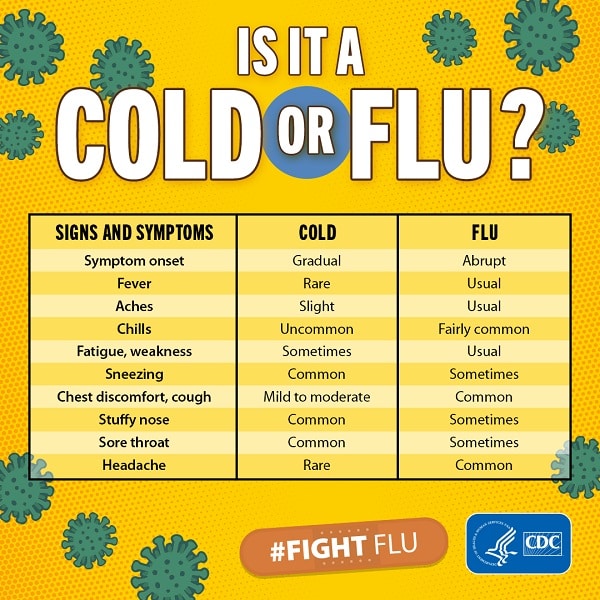
The symptoms of the flu can be mild to severe. They include a fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny nose, body aches, headaches, and/or fatigue. These sound pretty similar to the common cold, right? It can be very difficult to distinguish between the two. Blood tests or saliva tests can diagnose the flu or Covid-19, but there are no tests to diagnose the common cold. The flu and the common cold are both contagious diseases originating in the respiratory system, but the virus that causes each is different. The flu is only caused by an influenza virus. The common cold can be caused by a variety of viruses, from rhinovirus to a seasonal coronavirus. (Note: this is not the same as COVID-19). Check out the infographic below for more information on the distinctions between the two viruses.
Flu FAQs
How does the influenza virus spread?
The flu can spread by droplets - whether it’s from a sneeze, a cough, or a conversation. Like COVID-19, the distances can be within 6 feet. The droplets then land in the mouth or nose of the uninfected person, who then can inhale the virus into their lungs.
How long can I be contagious?
You are most contagious in the first 3-4 days of the illness. Adults can infect others from one day before the symptoms develop to 5-7 days after getting sick. Those with weaker immune systems can spread the virus for longer than 7 days. If you are running a fever, you are definitely contagious, but you can still be contagious without a fever. Many fitness trackers have the added function of tracking your temperature for you. The Oura ring tracks even slight variations in temperature and can be a good way to tell if your body is fighting an infection.
Who should I avoid when I’m contagious?
Ideally you should be avoiding everyone. However, those with weakened immune systems are the most at risk. Elderly friends or family and those who have immune-system illnesses should be avoided. Although this may seem like isolation or quarantine, it is an effective way to decrease the spread of a virus.
What are the 3 stages of the flu?
Day 0: you are contagious, but show no signs or illness. You may notice a slight feeling of fatigue or sore throat, but it is mild if noticed.
Days 1-3 are marked by fever, exhaustion, body aches and sore throat. Your body (immune cells) are spending a lot of energy killing infection in your body. Your throat hurts because your throat glands are full of dead viruses that have been killed by your immune cells.
Days 4-7 are the recovery phase days. You no longer have a fever, but your body is still devoting a lot of energy to fighting infection and inflammation.
What is the best way to prevent getting the flu?
There are many helpful strategies for avoiding the flu. Strengthening your immune cell function not only helps with cold and flu viruses, but can also prevent other more serious infections. Optimal vitamin D levels are vital for immune cell function. Zinc and vitamin C have both been proven to shorten the duration of a viral infection. Beta Glucan is an excellent support for your NK (natural killer) cells. 
The flu shot is the CDC’s recommended prevention for the flu. But it only has varying levels of effectiveness from year to year. Read more about it here.
However, there are other ways to prevent illness that you can do everyday. These include washing your hands often throughout the day, covering your mouth when you cough, and avoiding sugar treats. Read more about the 12 Tips for Prevention in this article.
How do I treat the flu?
If you get the flu, depending on your health, there are some treatment options that can be the difference between bed rest and a hospital stay. Higher risk individuals, like young children and those over 65, should monitor their flu symptoms and contact their doctor if needed. The CDC has a guide for what to do if you get the flu available HERE. They have included emergency warning signs that warrant immediate medical attention as well as a distinction between what does and does not warrant an emergency room visit.
Antiviral drugs can lessen the severity of symptoms and potentially shorten the amount of time you are sick. Additionally, they can prevent the flu from turning into pneumonia. These medications are provided by a prescription written by your doctor. They can come in the form of a pill, liquid, IV, or a powder. It is important to include, however, that antiviral drugs are not a replacement for prevention and a strong immune system. Antivirals are a second line of defense. Children can take antivirals, but it varies by medication.
What is the difference between the flu and COVID-19?
While the flu and COVID-19 are both infectious respiratory diseases, they are actually caused by different viruses. The flu is caused by an influenza virus and COVID-19 is caused by a coronavirus identified in 2019. Because the symptoms are so similar for both illnesses, going off of symptoms alone cannot give you an exact answer of which illness you may have. Testing needs to be done. Most cities and counties now have rapid nasal or blood tests available. Symptoms can show in a person infected by COVID-19 2 - 14 days after infection. With the flu, however, a person can experience symptoms 1- 4 days after infection.
There are two symptoms of Covid that are uncommon with flu viruses. Loss of smell and loss of taste are unique to Covid and seem to be hallmark symptoms setting it apart from influenza viruses.
Does the flu shot affect the effectiveness of my COVID-19 vaccine? (and vice-versa)
Because there has been no safety studies on the Covid vaccine, it is too early to tell whether or not it will interact with the flu vaccine.
How long does the flu last?
Symptoms of the flu usually appear 1-4 days after exposure and last for a total of 5 -7 days, on average. This may vary with those who have a weaker immune system.
In general, Covid-19 lasts longer than the flu. Most people will get over Covid in 2-4 weeks which is much longer than the usual flu viruses. Up to 33% of people who get Covid, develop long-haul symptoms, which is not common for influenza viruses.
What is Flu A vs. Flu B?
There are actually four different types of Influenza/Flu viruses. Flu A and B are the two types that cause seasonal infections every year in humans. While Flu B can only be found in humans, Flu A can be found in many different species. An example of Flu A is H1N1. Flu C mainly occurs in humans, but can also be found in dogs and pigs. Flu D is found in cattle.
Further Reading/Watching
The CDC compiles data frequently regarding the flu, the flu vaccine, and how various populations in the United States are being affected. For more information, check out their:
Take a look at this timeline for a look at how influenza viruses have affected people worldwide over time.
There is also a docuseries on Netflix about the flu - “Pandemic: How to Prevent an Outbreak”
Interested in the 1918 Flu Pandemic? The BBC has an audio documentary available for listening here.
Concluding Thoughts
Influenza has ravaged humanity for generations. From health impacts to socioeconomic influences. Influenza has the ability to touch our lives in one way or another. It’s influence is so great that in 2003, the total economic burden of influenza pandemics in the United States was $87.1 billion. This accounted for lost work time and increased usage of medical resources. It’s nothing to take lightly. I hope this informational guide on the flu/Influenza was helpful to you in some way - if you have questions about how best to strengthen your immune system or the best ways to prevent the flu - Schedule a consult with me, Carly Neubert BA, NC. 

